Renal #
Hypertension (HTN) #
| Classification | SBP/DBP |
|---|---|
| Low | <90/<50 |
| Normal | <120 AND <80 |
| Elevated | 120-129 AND <80 |
| Stage 1 HTN | 130-139 OR 80-89 |
| Stage 2 HTN | ≥140 OR ≥90 |
- Measured on at least two occasions
- Ambulatory BP measurements good, have pts do them
- Cuffs to get (link/table???)
- Some data suggest that taking BP meds at night (save loops) has better outcomes.
RAAS System #
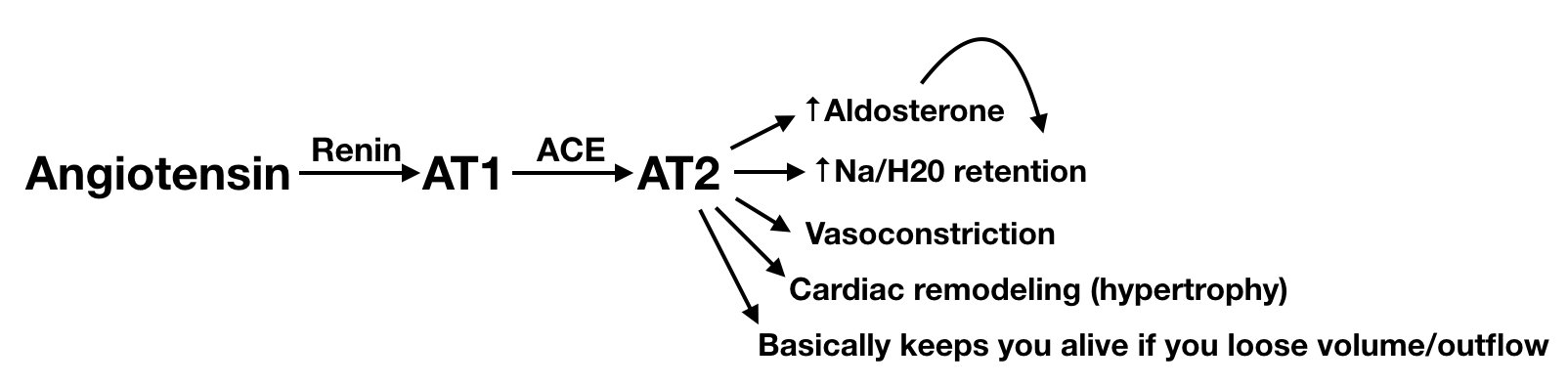
Drug Classes #
| Class | Mechanism | AEs | Contraindications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACE | blocks formation of Angiotensin II (and degradation of bradykinin) | cough, rise in SCr, HyperK | pregnancy, bilat renal artery stenosis |
| ARB | blocks Angiotensin II receptors | rise in SCr, HyperK | pregnancy, bilat renal artery stenosis |
| dihydro-CCBs ("-pines") | prevents vascular constriction (does not relax them) | flushing, edema | HF w/ edema (w/o ok, but caution) |
| non-dihydro-CCBs (dilt and verapamil) | Cardiac slective relaxive effect | bradycardia, arrythmias | |
| BBs (Mixed, have alpha activity too) | block peripheral alpha receptors | BBflu, sexual dysfunction (~50%) | |
| Thiazides | resets body’s fluid “set point”; inhibits Na reabsorption in distal tubules | ↓K, gout, retain Ca, hypoNa | GFR <30 |
| Loops | Inhibits NaCl in asceinding loop | sulfa | Not a BP med, just gets fluid off |
| Central alpha agonists (clonadine) | a2 stim in brain, ↓ sympathetic outflow | hypoTN, fatigue/sedation | |
| Direct vasodilators (hydralazine) | Unknown, direct arterial dilation | Drug-induced lupus, HA, hypoTN | |
| Alpha-1 blockers ("-zosins") | blocks peripheral alpha receptors | orthostatics, nasal congestion | |
| Aldosterone Antagonists | aldosterone competition, useful in aldosterone escape | hypoK esp. w/ ACE/ARB, gynecomastia (spiro only) |
Drug Preference Order #
| Scenario | ACEi/ARB | CCB | Thiazide | Ald. Antag. | BB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| CAD | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| HF | 1 | 21 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| CKD | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| H/o CVA/TIA | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| DM | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Osteoperosis | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
Special situations:
- Angina: CCB or BB
- Afib/flutter: metoprolol or nd-BB
- BPH: alpha-1 blocker
- Essential tremor: BB, propranolol
- Hyperthyroidism: BB
- Migraines: BB, propranolol, metoprolol
- Reynaud’s: nd-CCB, nifedipine
ARBs #
| Strength | ARB |
|---|---|
| Weakest | Losartan |
| Moderate | Valsartan |
| Moderate | Irbesartan |
| Strongest | Olmesartan |
Above table is general, probably not clinically significant. Generally, recommend olmesartan.
AKI #
Dx:
- ↑ SCr > 0.3 mg/dL or 1.5x baseline or
- Urine output < 0.5 mL/kg/hour for 6 hours
Workup:
- Labs
- UA
- BMP/RFP
- Urine Osms
- Urine Na, Cr
- Renal US
DDx:
- US
- If hydro → obstruction
- If small, echogenic → AKI on CKD
- If normal then
- Oliguria or otherwise volume down?
- FeNa >1% and UOsm <350 mOsm/kg, muddy casts → ATN
- FeNa <1% and UOsm >350 mOsm/kg, hyaline casts → prerenal azotemia
- Normal volume status
- UA
- Fever, rash, WBCs → Interstitial nephritis
- Dysmorphic RBCs, RBC casts, proteinuria → Glomerulonephritis
- Check ANCA, anti-GBM, C3, C4, hepatitis
- UA no cells, protein → p/c, SPEP, UPEP
- UA
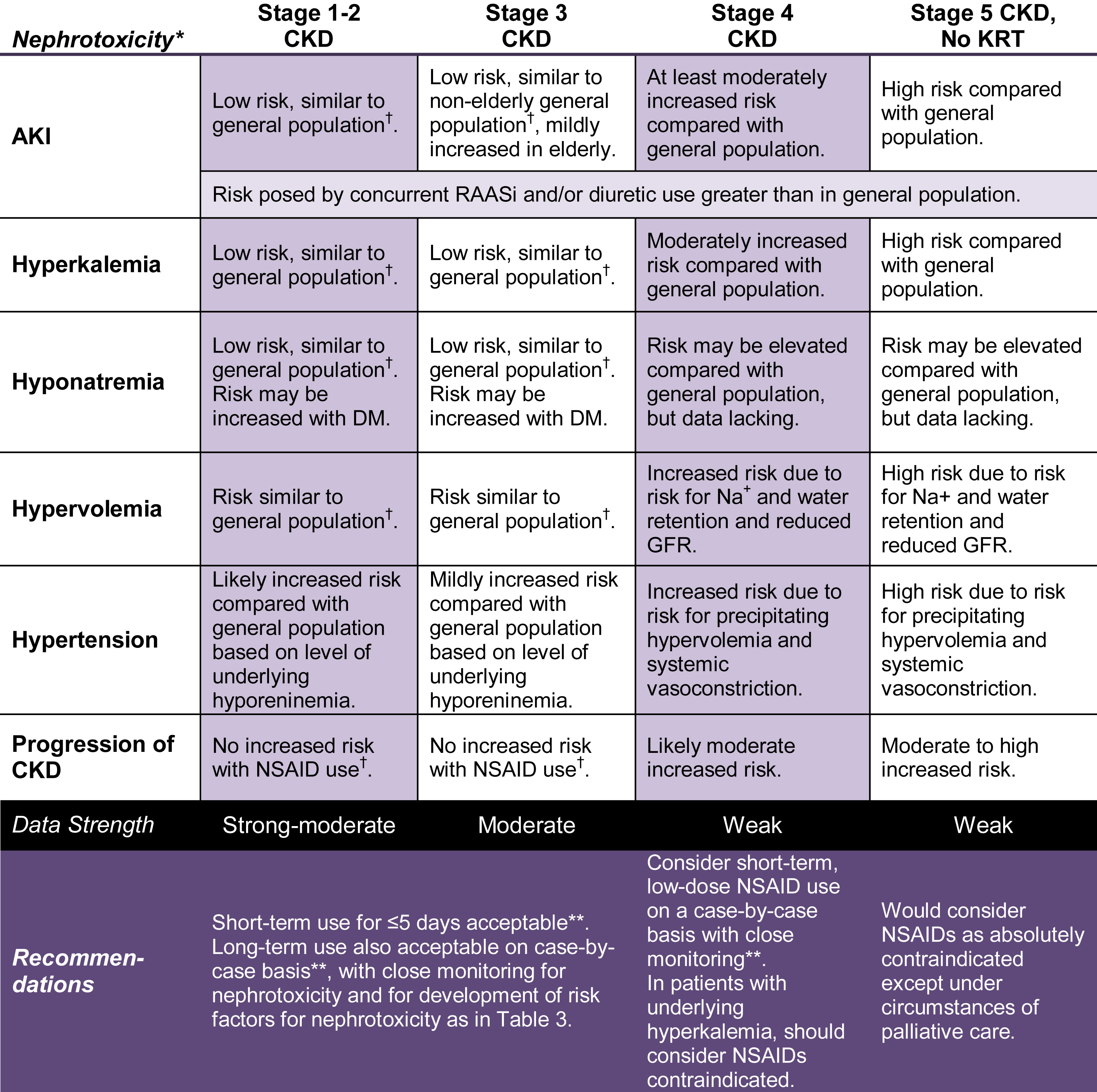
CKD #
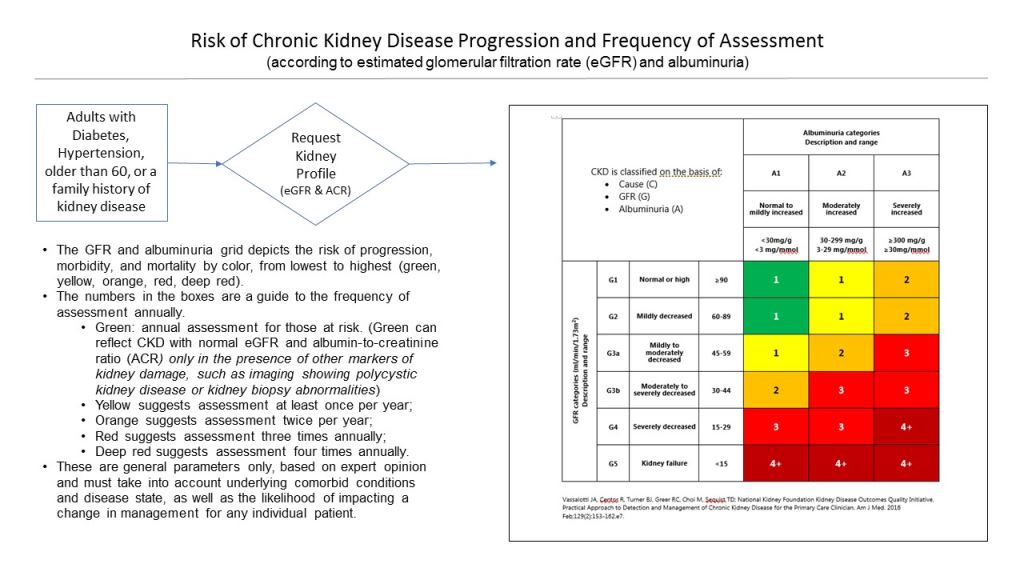
NSAIDs in CKD #
Specific risk factors that put patient’s at higher risk.
Orthostatics #
- SBP decrease >20mmHg
- DPB decrease >10mmHg
- HR increase >30BPM Any one true = positive orthostatic test
Treatment #
- Midodrine
- Florinef
Diuresis #
Prominent side effect of diuresis: cramping (pull back)
Diuresed urine is approximately 1/2 NS with 20mEq K.
- Lasix (fursomide)
- 20-80mg q6-8h PO (max 600mg/day in severe edematous states)
- 20-40mg q1-2h IV (max 200mg/day)
- 2x SCr is a good ballpark place to start with IV dose for diuresis
- Bumex (Bumetanide)
- 0.5-2mg 1-2x/day, can repeat after 4-5hrs (max 10mg/day)
- 0.5-1mg, can repeat in 2-3hrs (max 10mg/day)
- Demadex (torsemide)
- 10-20mg starting, usually need 20-40mg
- Max 200mg/day
- Metolazone (thiazide)
- 5-10mg PO Qday (max 20mg/day)
- Dosed before loop for combinatory effect
Dialysis #
Indications for urgent/emergent dialysis: AEIOU
Acedemia
Electrolyte abnormalitites
Intoxicated
Overload (volume)
Uremia
Fluids #
Maintenence Rate #
Ballpark rule of thumb:
- Weight in kg x 1-2 = maintenence rate
- 1 is more gentle
- 2 is more agressive, but not a resuccitation
Sodium (Na) #
Hypernatremia #
- AMS
- Seizures
- resp arrest (rare)
Signs/Symptoms #
Workup #
- Hypovolemic
- Urine Osms >800 AND FeNa2 <1% → extrarenal loss of Na and water
- N/V/D
- Sweating/burns
- Mechanical ventilation
- Urine Osms 300-800 → renal loss
- Diuretics
- Osmotic diuresis
- Partial DI
- Urine Osms >800 AND FeNa2 <1% → extrarenal loss of Na and water
- Euvolemic
- Urine Osms <300 → DI, do desmopressin challenge test
- If responsive → central DI
- If resistant → nephrogenic DI
- Usually caused by hypercalcemia, hypokalemia or meds (lithium)
- Urine Osms 300-800
- Partial DI
- Osmotic diuresis
- Primary hypodipsia
- Urine Osms <300 → DI, do desmopressin challenge test
- Hypervolemic
- Ingestion of salt (sea water)
- Primary aldosteronism
- Iatrogenic (hypertonic saline, HD errors)
Treatment #
- D5W +/- lasix (with lasix usually an ICU only thing)
- Correct serum sodium by 1 mmol/L/hour in the first 6-8 hours
Hyponatremia #
Signs/Symptoms #
Workup #
- Serum Osms
- <280? → clinical volume status
- Hypovolemic
- Urine Osms >500 mOsm AND UNa < 20 AND FENa <1% => extrarenal
- Urine Osms >500 mOsm AND FENa >1% => renal loss
- Euvolemic (urine Na usually >20-30)
- Rule out hypothyroidism and adrenal insufficiency
- Urine Osms >100 => SIADH
- Urine Osms <100 => primary polydipsia, beer potomania
- Hypervolemic
- UNa <20-30mmol/L AND FeNa <1% => HF, cirrohsis w/ ascites, nephrotic syndrome
- UNa >30 => renal failure or diuretic use
- Hypovolemic
- 280-295?
- check for pseudohyponatremia
- Sodium correction for glucose calculator
- >295?
- check serum glucose
- <280? → clinical volume status
Treatment #
- Water restriction (i.e. cause is too much free water)
- Saline infusion (i.e. cause is not enough solute)
- Can use NS, LR
- 3% saline only if symptomatic
- Goal correction 6-8mEq/24hrs
- Avoid central pontine mylinolysis (CPM)
- Very low chance of CPM after Na hits 125
- Infusion rate calculator
- Be conservative with this, likely oversimplification of the biology in the math
- Can use NS, LR
Potassium (K) #
- 10mEq KCl should raise serum K 0.1 (with normal kidneys)
- Can only absorb ≈60mEq q8h
Hyperkalemia #
Signs/Symptoms #
Treatment #
- CaCl2 (transient)
- Albuterol
- D50 + insulin
- Bicarb
- Kayelxylate
- Diurese
Calcium (Ca) #
Hypercalcemia #
- Total calcium > 10.5 mg/dL, or ionized > 5.6 mg/dL
- Mild: 10.5-12
- Moderate: 12-14
- Severe: >14
- Often asymptomatic, if symptomatic likely moderate to severe (also likely rapid rate of change)
Causes #
- Hyperparathyroid or Malignancy (two most common)
- Granulomatous diseases
- sarcoidosis
- berylliosis
- coccidioidomycosis
- TB
- histoplasmosis
- leprosy
- inflammatory bowel disease
- foreign body granuloma
- Vitamin D, Vitamin A excess
- Meds
- Thiazides
- Lithium
- Vitamin A (accutane?)
- Antacids (Tums)
- Some bengin tumors
- Endocrine
- hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis
- adrenal insufficiency
- acromegaly
- pheochromocytoma
- Verner-Morrison syndrome
Measurement #
- Must always correct for serum albumin (≈50% bound)
- If not normal serum pH, use ionized calcium (correction formulas assume normal pH for binding energetics)
- Ionized can also help suss out false positives
Workup #
- PTH
- If normal/high => GFR, 24hr urine Ca, creatine
- GFR < 60 will have increase in PTH
- CaCrCL < 0.01 => familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (80%)
- CaCrCL 0.01-0.02 => primary hyperparathyroidism (≈ 20% fam hypocal hypercal)
- CaCrCL > 0.02 => primary hyperparathyroidism
- If low
- => malignancy eval (CT, sekeletal survey, PET, etc.)
- Can sometimes be something endocrine
- If normal/high => GFR, 24hr urine Ca, creatine
Signs/Symptoms #
- bone pain
- nausea/vomiting
- anorexia/weight loss
- constipation
- abdominal pain
- obtundation, confusion, delirium, or memory loss
- lethargy/fatigue
- muscle weakness
Treatment #
- IV NS
- Bisphosphonates
- pamidronate 60-90 mg IV/4hrs, zoledronic acid 4 mg IV/15min
- Takes a day or two to kick in
- Effect can last for weeks
- calcitonin
- 4 units/kg subq/IM q6-12hrs x 24 hours
Consider Denosumab (If bisphosphonates not working), steroids (vitamin D excess, granulomatous disease, or hematologic malignancies).
Complications #
- Renal
- renal tubular acidosis
- nephrolithiasis
- nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
- nephrocalcinosis
- CKD
- GI
- constipation
- pancreatitis
- peptic ulcer disease
- Neuromuscular
- impaired concentration and memory
- dementia
- muscle weakness
- CV
- hypertension
- shortened QT on EKG
- arrhythmias
- vascular calcification
- valvular heart disease
- HEENT
- corneal calcification (band keratopathy)
Hypocalcemia #
| Cause | PTH | Phos | Alk Phos | 25-OH Vit D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renal | ↑ | ↑ | ↔/↑ | ↔/↓ |
| Vit D deficient | ↑ | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ |
| Vit D resistance | ↑ | ↓ | ↔ | ↔ |
| Hypoparathyroid | ↓ | ↑ | ↔ | ↔ |
| PseudoHypoparathyroid | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ | ↔ |
| HypoMg | ↔/↓ | ↔ | ↔ | ↔/↓ |
| Bone mets | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↔ |
| Ca-sensing receptor defect | ↔ | ↔ | ↔ | ↔ |
Toxicity #
- Vanc/Zosyn approximately 4x (HR 2.73–6.68) more likely to get AKI than with Vanc/Cefepime (Paper)
The Nephron #
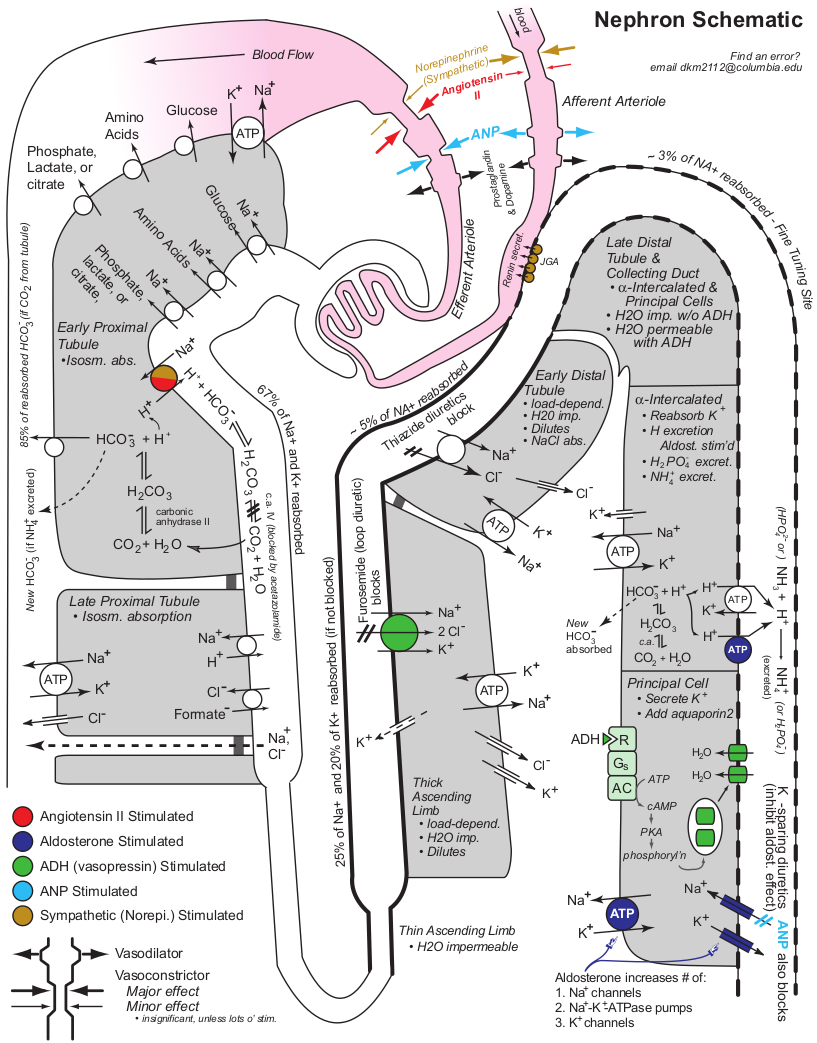
Pearls #
- Lisinopril => teratogenic, caution in young women
- Use renal diet only in ESRD (CKD can handle normal diet)
- Losartan decreases gout (only losartan, not all ARBs)
- Phos repletion is 100% feel, no rules like K
- Reach for labetalol instead of hydralazine for BP control in CKD/ESRD
- Response to hydralazine really varies from not working at all to bottoming people out