Critical Care #
Good References:
Sepsis:
- First thing to go: Lactate, Cr
- First thing to get better: Lactate
Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI) #
- ETT 7.5
- Etomidate 20mg (+/- 2-4mg versed IV)
- Rocuronium: 1mg/kg (OR Vecuronium: 10mg fixed, or Succinylcholine 1.5mg/kg)
- Checklist:
- Bag (make sure you can bag before giving paralytic or you’re F-ed)
- Suction
- Meds
- ET Tube (plus spare)
- Vent/RT
Sedation meds (all given as IV bolus): #
- Etomidate: 0.15-0.3mg/kg, 20-30mg usually
- Onset 30-60sec, duration 3-5mins
- Lowers seizure threshold?
- Causes release of cortisol, can have rebound hypotension ˜24hrs later
- Inhibits cortisol, caution in adrenal insufficiency
- Ketamine: 2mg/kg
- Onset 1-2min, duration 5-15mins
- Avoid with increased cranial pressures (closed intracranial trauma, ↑ intraoccular pressure, CAD, HTN)
- Propofol: 0.5-2mg/kg
- Onset 9-50sec, duration 3-10mins
- Can cause hypotension, just bolus with fluids at same time and it’ll be ok
- Egg and soy allergies
Paralytics #
- Succinylcholine: 1.5mg/kg
- Onset 30-60sec, duration 5-15mins
- Don’t use if hx of malignant hyperthermia or life-threatening hyperkalemia
- Rocuronium: 1mg/kg
- Onset 1-2mins, duration 45-70mins
Confirming Placement #
- ET tube tip should be between 2-5cm from carina.
- Examples with anatomy
Dr. Amir’s Setup #
- ETT 7.5 (7-8)
- good for almost everyone
- Etomidate 20mg
- +/- versed 2-4mg
- Paralytic
- Make sure you can bag before you give paralytic
- If not, you are screwed if you give paralytic and can’t intubate
- Rocuronium: 1mg/kg
- Vecuronium: 10mg fixed
- succinylcholine: 1.5mg/kg
- Careful as can raise K, not great for renal failure Get a PEEP valve on bag mask (helps you get peep when bagging, really need this for ARDS, when you take off HHF sats will tank)
- Make sure you can bag before you give paralytic
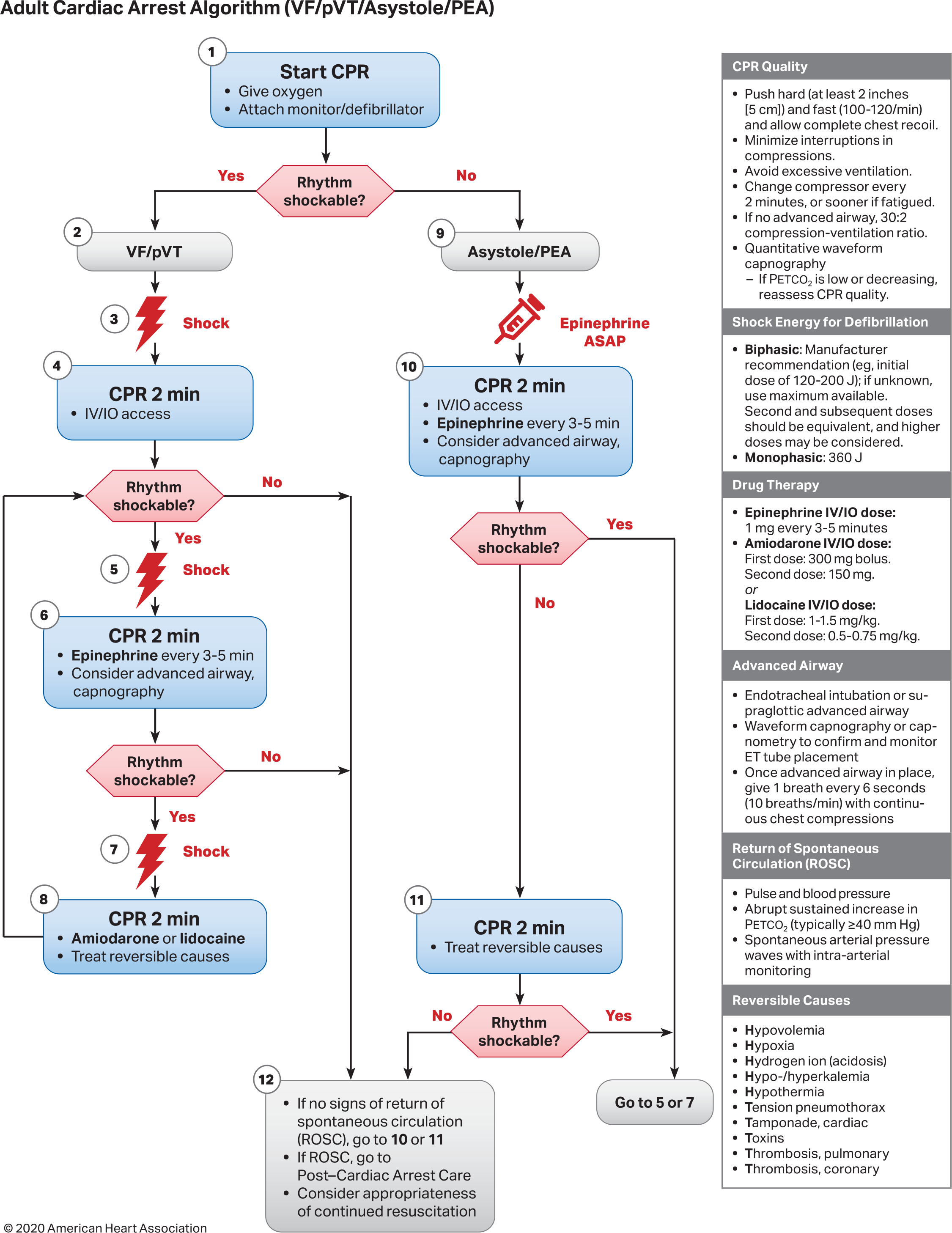
ACLS (Adult) #
Arrest #
Bradycardia #
- Eval
- ABCs
- O2
- IV
- EKG
- Stable
- Monitor
- Unstable
- Atropine 1mg (q3-5mins, max 3mg)
- Epinepherine gtt: 2-10mcg/min
- Dopamine gtt: 5-20mcg/kg/min
- Transcutaneous pacing
- Atropine 1mg (q3-5mins, max 3mg)
Tachycardia #
- Eval
- ABCs
- O2
- IV
- EKG
- QRS complex width
- Narrow (<0.12)
- Stable
- Vagal maeuvers
- Adenosine
- 6mg then 12mg (can go higher in real life)
- Unstable
- Sync cardioversion
- Adenosine
- Stable
- Wide (>0.12)
- Stable
- Adenosine (only if regular and monomorphic)
- Procainamide 20-50mg/min (max dose 17mg/kg)
- Unstable
- Sync cardioversion
- Stable
- Narrow (<0.12)
Stroke (CVA) #
- ABCs, O2 if needed
- Check glucose
- CT/MR
- IV
Goals:
- Gen assessment: 10 mins
- Neuro assessment and CT/MR: 20 mins
- Rads read: 45mins
- lytics within: 60 mins from ED door
- lytics within: 3-4.5 hrs of symptom onset
- EVT (endovascular therapy)
- LVO: 24 hrs
- 0-6hrs: CT findings
- 6-24hrs: penumbral scan
- Admission to bed: 3 hrs
- Transfers: 1 hr
AMI #
- if O2 < 90% → 4L
- ASA 162-325mg
- Nitro (careful with RV ischemia, pre-load dependent)
- Morphine IV (careful with RV ischemia, pre-load dependent)
Goals:
- Door to balloon: 90 mins
- Door to needle (lytics): 30 mins
ROSC #
- Breaths: 10+/min
- SpO2: 92-98%
- PaCO2: 35-45 mmHg
- SBP >90, MAP >65
- EKG → if STEMI or LBBB cards intervention
- Follows commands?
- No
- TTM (32-36C) x 24hrs
- CT head
- EEG
- Yes
- ICU management
- No
BLS #
- Adults:
- Breaths: 1 every 6 sec
- 30-2
- If pregnant to umbilicus, laterally displace uterus
- Peds:
- Breaths: 1 every 2-3 sec
- One rescuer
- 30-2
- Leave after 2 mins to get AED
- Two+ rescuers
- 15-2
Vent Management #
Three modes to know:
- VC
- Good for COPD, asthma since you can control the I:E ratio
- VC+ (PRVC)
- Pressure regulated volume control
- Good general purpose
- APRV
- Inverted I:E
- Oxygenation
- FiO2
- PEEP
- Ventilation (i.e. CO2)
- tidal volume
- rate
- combination of which is your minute ventilation
Changes #
Winter’s formula:
$P_{CO_2} = 1.5 * HCO3- + 8 +/- 2$
Then figure your change as CO2 is proportional to rate and tidal volume.
$CO2 prop rate * V_T$
Plateau pressures should be <30
tidal volume should be 6-8cc/kg ideal body weight
Sedation on Vent #
-
Important to differentiate between anxiety and delirium, sometimes hard to tell the difference
-
[PADIS 2018 guidelines](’/literature/PADIS 2018 guidelines.pdf')
-
Precedex
- Awesome med, can be continued post extubation
- Quick and clean on and off
- Not a sedative, it’s an anxiolytic
- Can cause bradycardia/hypotension
- Not a huge issue, but be aware of it
- Transition to clonidine if going to be used for more than 7 days
- Awesome med, can be continued post extubation
-
Propofol
- Great for short term (<3-4 days) as is a sedative
- switch to fentanyl/versed pushes if you need longer
- Quick on, quick off
- Has some GABA activity
- Good choice in EtOH withdrawl and/or seizures
- Watch for propofol infusion syndrome
- Looks like shock without a source
- ↑ CK
- ↑ lactate (12-14ish)
- ↑ Chol, LFTs
- hypotension
- green urine (boards only really)
- usually happens to people on high doses (>100/hr) and long durations (>3-4 days)
- Looks like shock without a source
- Not great in fat people, gets stored in fat
- Great for short term (<3-4 days) as is a sedative
-
Ketamine
- Need to learn more here…
-
Always favor narcotic pushes over drips
-
Last resort is benzos
- Almost never use benzo drips
Paralytics #
Almost always use Cisatracurium.
- Cleared by Hoffman elimination, not eliminated by kidneys or liver.
Anxiety #
- Talk to family, ask if pt with history of anxiety
- Benzos great for anxiety, crappy for delirium (can make it worse)
Delirium #
- Definition: imparied attention (that’s it!), usually acute onset (vs dementia)
- Important as is independent risk factor for mortality
- Evidence to suggest that it’s an inflammatory brain process (from autopsies)
- Important for healing, not just for making out and RNs lives easier
- Hyperactive and hypoactive flavors
Treatment #
- haloperidol (Haldol)
- 0.5-20mg q15-30mins until calm
- olanzapine (Zyprexa)
- 5-10mg IM, max 30mg/day
- ziprasidone (Geodon)
- 10mg IM q2h or 20mg q4h, max 40mg/day
- 20-40mg PO q12h
- quetiapine (Seroquel)
- 50mg PO BID, max 400mg/day
Also Qtc prolongers
Watch for serotonin sydrome with above meds: - fever, rigitity - Check CPK,
Central Line #
Nasogastric tube (NG/Dob-hoff) #
ECMO #
- VV = all on right side
- Code => normal
- VA = take from right side, return to arterial side
- Code => just fix heart
- Sweep = speed of gas (O2) in exchanger
- Basically equivalent to minute ventilation (think of it like resp rate on vent)
- Increase this to take off more CO2
- FsO2 = just like FiO2
- Doing good if sweep <2, and FsO2 as low as can go
Acute hypoxia #
- Causes:
- Parenchymal => pulm edema, atelectasis/shunt
- PE
- Cardiac => MI, arrhythmias
- Hypercarbia => displaces O2
Chronic hypoxia #
- Causes:
- CHF
- pHTN
- Lung disease
- CO2
- Shunt
Workup #
- ABG => looking at pCO2, paO2
- PFTs (full): dlCO, plus underlying lung disease
- CT => structural lung disease (CXR good quick and dirty look, but can miss a lot)
- Echo w/ bubble => cardiac causes
- EKG
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) #
- Acute onset hypoxemia with bilateral radiographic infiltrates (no LA hypertension)
- Dx needs three things:
- Onset within one week of known insult
- Bilat opacities on CXR => not effustions, or otherwise explained
- Resp failure not from fluid overload or some other cause (i.e. cardiac causes)
- Decrease in lung compliance
- Insults usually cause direct lung injury
- PNA
- Aspiration
- Massive rapid transfusion (TRALI)
- Non-pulm sepsis
- Severe trauma
- Dx needs three things:
Severity #
| Severity | PaO2/FiO21 | Mortality |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | >200mmHg | 27% |
| Moderate | 100-200mmHg | 32% |
| Severe | <100mmHg | 45% |
Evaluation #
- r/o other causes of sepsis
- ABG
- CXR/Chest CT
- Echo + pBNP (r/o cardiac causes)
- Bronch
Treatment #
- Mechanical vent
ARDSnet table #
| FiO2 | Low PEEP | High PEEP |
|---|---|---|
| 0.3 | 5 | 5-14 |
| 0.4 | 5-8 | 14-16 |
| 0.5 | 8-10 | 16-20 |
| 0.6 | 10 | 20 |
| 0.7 | 10-14 | 20 |
| 0.8 | 14 | 20-22 |
| 0.9 | 14-18 | 22 |
| 1.0 | 18-24 | 22-24 |
Usually use high PEEP for COVID-19.
Airway Pressure Release Ventiliation (APRV) #
EMCrit explanation article and settings/strategy.
- Good for reqruitment
- Not great for "floppy lung" diseases (COPD, asthma)
- Best for stiff lungs (i.e. ARDS, pneumonia, some ILDs)
- Typical start
- P-high: 30-35cm
- P-low: zero
- T-high: 5 sec
- T-low: 0.5 sec
- reduce if tidal volume >8mL/kg
ABGs #
- pCO2 normal range:
- Men: 36-40
- Premenopausal Women: 34-36 (even lower in pregnancy)
- pO2 normal range:
- Denver: 70-80
- VBG
- Tells you everything except for oxygenation
- To “correct” to an ABG
- Peripheral
- pH: add 0.02-0.04
- pCO2: subtract 3-8mmHg
- Central
- pH: add 0.03-0.05
- pCO2: subtract 4-5mmHg
- Peripheral
- SvO2
- Normal: >65% (normal O2 extraction ≈25-30%)
- <65% => imparied tissue oxygenation
- >80%
- High PaO2
- Cytotoxic dysoxia
- severe sepsis
- cyanide poisoning
- mitochrondial disease
- Microcirculatory shunting
- severe sepsis
- liver failure
- hyperthyroidism
- Left → right shunt
Volume Status #
Assessment of volume status in criticall ill
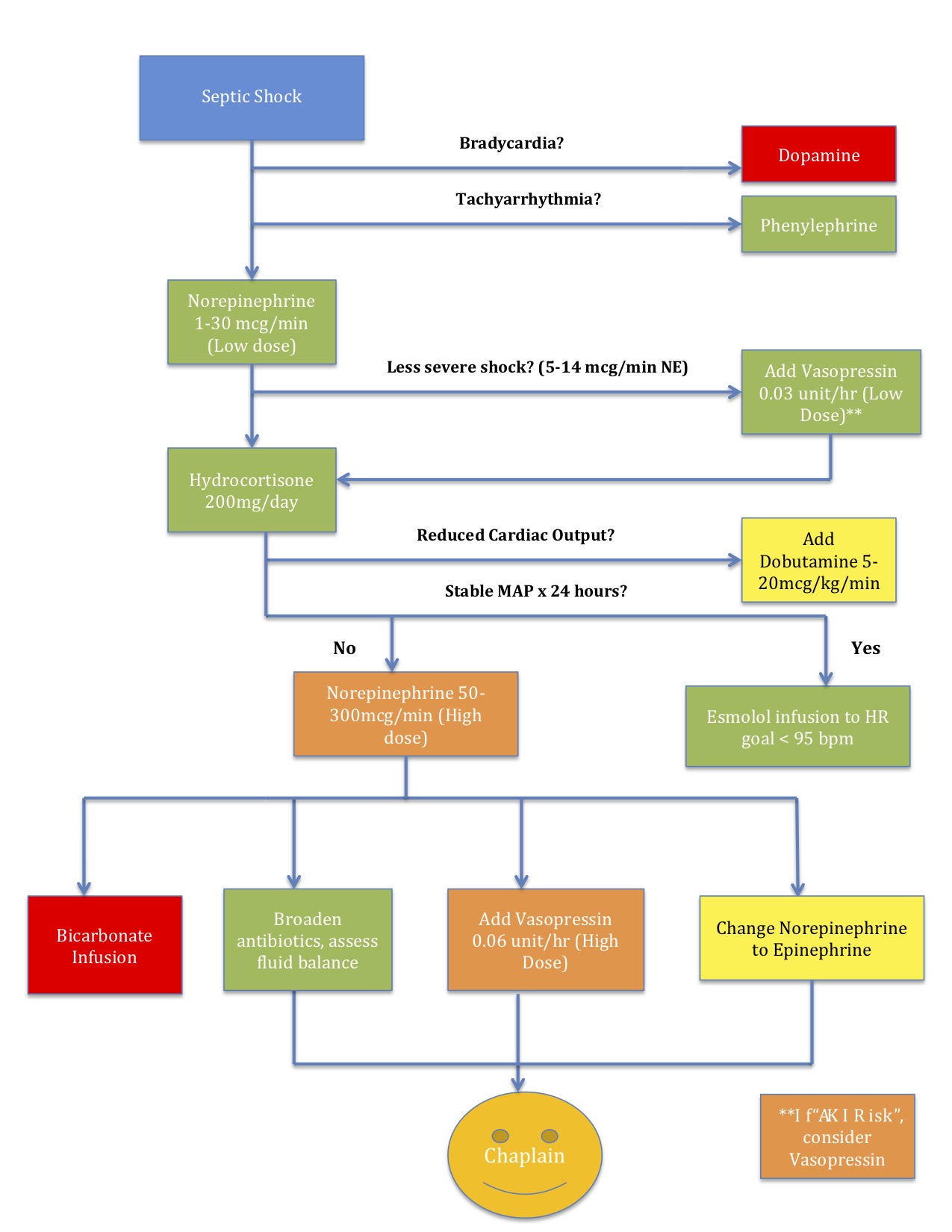
Septic Shock #
Anaphylactic Shock #
- Epipen q5min
- Epi drip with “dirty” epi
- “Dirty” epi
- 1mg epi in 1000mL NS
- Start at 1mL/min
- Titrate to symptoms and BPs
- “Dirty” epi
- Adjuncts
- Methylprednisone 125mg IV
- Diphenphyramine 2mg/kg (50mg max)
- famotadine 20mg IV (or other H2 blocker)
Pearls #
- Palpate posterior upper leg for edema in ICU patients (most dependent spot)
- Every 10 CO2 increase => 1 bicarb increase
- Sats above 80 are OK! As long as normal WOB, mentating normally.
- Stress Dose Steroids: Hydrocort 50mg q8h until shock gone
- Angor animi => medical term for “sense of impending doom”
-
with PEEP/CPAP > 5cm H20 ↩︎